While South Ossetia has declared itself a nation independent of Georgia (much to Georgia's ire), it seems to be more reliant on Russian foreign aid and military assistance more than ever.
Thousands of Russian troops guard both the country and it's borders, and "Russian aid compromises 99% of South Ossetia's budget since 2008." This is obviously not the mark of a healthy, independent nation but that of a satellite state that would decay into a 3rd world state if foreign aid were ever cut off.
This of course is an understandable situation for a war torn country that broke off and became independent only years ago. Unfortunantly, corruption stains the government of South Ossetia, to the point where elections are dangerous especially for the candidate opposing the Russian-backed leader. Alla Dzhioeva won the elections that were held in November of 2011, but Anatoli Bibilov maintained Russian support even if more than 50% of the population voted for Dzhioeva. Eventually, the supreme court ruled in favor of Anatoli and Dzhioeva argued against this, demanding inauguration by February 10th. Oddly enough, she was attacked by masked men soon after this, and remains hospitalized at this time. By no means does this incriminate Russia, as Dzhioeva was very pro Russia and pro Putin. However, the people of South Ossetia now harbour some level of suspicions against their benevolent providers, as they realize that Russia is not always a "honest broker".
Georgia still has no part in what they consider Russian occupied territory, and relations are as poor as ever for them. It seems that the fate and future of the relatively new independant South Ossetia lies not in the hands of it's people and politicians, but at the Kremlin.
Thursday, December 13, 2012
Cause and Effect: Who Started the South Ossetian War?
The South Ossetian War that occured in late 2008 was a diplomatic crisis for the entire world, especially considering that it took place during the Olympics and many world leaders attentions were divided. Lots has been said about the cause of the war and whether or not Georgia or South Ossetia, or even Russia started it. In Europe however, a fourth name has been brought up: the United States.
Georgian President Mikheil Saakashvili has his ties to the American government, having graduated from an American Law School and worked at a law firm in New York City before he became the leader of Georgia. Even during the 2003 Rose Revolution that ousted his predecessor, Saakashvili had recieved funding from the American government, and has since received much more funding over the past few years.
While there are obvious ties to the American government, the United States can only be blamed so far. "State from President Bush and others may have emboldened Saakashvili to expect US assistance that in the end wasn't forthcoming, but that's a far cry from an active role in launching military action."
It's almost impossible to pin the blame on a single party, as it appears that both the United States and Russia we're using their respective allies in a modern version of a proxy war, like two soccer moms fighting vicariously through their kids during a game. Until more evidence comes to light, it appears that the world will have to settle with what it's got.
Georgian President Mikheil Saakashvili has his ties to the American government, having graduated from an American Law School and worked at a law firm in New York City before he became the leader of Georgia. Even during the 2003 Rose Revolution that ousted his predecessor, Saakashvili had recieved funding from the American government, and has since received much more funding over the past few years.
While there are obvious ties to the American government, the United States can only be blamed so far. "State from President Bush and others may have emboldened Saakashvili to expect US assistance that in the end wasn't forthcoming, but that's a far cry from an active role in launching military action."
It's almost impossible to pin the blame on a single party, as it appears that both the United States and Russia we're using their respective allies in a modern version of a proxy war, like two soccer moms fighting vicariously through their kids during a game. Until more evidence comes to light, it appears that the world will have to settle with what it's got.
Two-way Drone war
The conflict between Russia and Georgia seems to have started an unprecedented arms build up between the two counties. Except, instead of hoarding guns or nuclear armaments the counties have been seeking advanced drones.
When the South-Ossetian war started in 2008, Georgia initially had an advantage due to the advanced intelligence provided by their advanced Hermes-450 drones, which are nearly as technologically advanced as the Predator drones that the US military employs. Russia on the other hand was stuck using bomber and fighter jets in place of drones for surveillance before even getting access to actual drones. When Russia finally sent out their outdated drones, many were lost because of their outdated technology and were generally ineffective.
Russian officials said that the losses suffered due to the outdated drones was "calamitous" and have recently made a deal with Israeli defense contractors to upgrade their drones to more modern standards, ironically from the same source that Georgia's Hermes-450 Drones came from.
The conflict in the middle east has seen its fair share of drone warfare as well, but the vast majority came from the United States and were used against enemies of the American military. The South-Ossetian war was the first conflict where an actual drone war started, while Russia eventually won the conflict it was a messy victory for them partly due to the unreliable nature of their drones and surveillance compared to the advanced tech that Georgia had employed at the time.
http://www.globalpost.com/dispatch/news/regions/europe/russia/121022/russia-georgia-drones-little-war?page=0,1
Monday, December 10, 2012
Mahmoud Abbas avoiding negotiations
Since taking office in 2009, Prime Misnister Benjamin Netanyahu has extended gestures towards the Palestinians to encourge their return to the negotiating table with Israel. He has voiced in support of a solution for the conflict between the two states, Isreal and Palestinian. By doing this he has broken the policies of his predecessors. He enforced the freeze on constructions on the building of new Jewish homes in Judea and Samaria. For the stopping on construction to build homes, Isreal was asking for the agreement that they had signed, to be respected and for the Palestinian to have a readness to negotiate with them.
Palestinian Chairman Mahmoud Abass has avoided talking to the Isreal goverment. To make matters worse he is tring to talk with Hamas to reconcile their differences. Hamas has still been firing missiles on the Isreal cities and towns. Abass is also lobbing to the U.N. for unilateral recognition, insted of recognizing that Isreal exists as a Jewish State. This agreement could possible end the conflict between these two state.
Isreal calls for the support of the world to call for negotiation and resolvoing the confilcit. Rather that give in to Palestinian ploys that will lead to more distrust, hardship and conflict.
http://www.usatoday.com/story/opinion/2012/12/05/israel-netanyahu-danny-danon/1749705/
Palestinian Chairman Mahmoud Abass has avoided talking to the Isreal goverment. To make matters worse he is tring to talk with Hamas to reconcile their differences. Hamas has still been firing missiles on the Isreal cities and towns. Abass is also lobbing to the U.N. for unilateral recognition, insted of recognizing that Isreal exists as a Jewish State. This agreement could possible end the conflict between these two state.
Isreal calls for the support of the world to call for negotiation and resolvoing the confilcit. Rather that give in to Palestinian ploys that will lead to more distrust, hardship and conflict.
http://www.usatoday.com/story/opinion/2012/12/05/israel-netanyahu-danny-danon/1749705/
Global Conflict in The Age of Technology and Internet Piracy Part V
TorrentFreak Article on Kim Dotcom and Megaupload
As more and more people are learning to utilize the internet for a number of applications, friction has begun to arise between legislation and the general population. Kim Dotcom and his company which includes the website Megapuload have created a firestorm of bad press and harsh opinions of both Kim Dotcom and the United States government for their aid in illegal seizures of Dotcom’s possesions. Megaupload was described as, a cloud-based server space and file hosting where users could post their content and download it using a link. This website was closed down and all of Dotcom’s assets were seized during his arrest for copyright infringement, money laundering and a host of other accusations.
Popular opinion has been that his website was removed and his campaign for Megabox.com (where artists would be able to sell their music directly to consumers and keep up to 90% of the profits) was crushed because of influence from the MPAA, RIAA and the like from fear of change. Kim Dotcom writes in his post on Torrentfreak.com, “Megabox.com, a site that will soon allow artists to sell their creations direct to consumers and allowing artists to keep 90% of earnings...You can expect several Megabox announcements next year including exclusive deals with artists who are eager to depart from outdated business models.” (P.21-22) The business models being used for Mega and all of its subsidiaries are intriguing to say the least and I am interested to see how much more conflict comes with it. Conflict is all around us. I am excited to have shared a small portion of the conflict that interests me the most.
Global Conflict in The Age of Technology and Internet Piracy Part IV
The Atlantic Article on ACTA in a Global Capacity
Unfortunately, internet piracy has become such a common theme in media that it has reached the international arena. Legislation in many countries has been modified to include bills and amendments that discuss guidelines, definitions and consequences for internet piracy and copyright infringement. The Atlantic had this to say about it: “In the wake of the public outcry in the United States over proposed domestic antipiracy legislation, the Stop Online Piracy Act (SOPA) and the Protect IP Act (PIPA), international regulation is also taking a hit. The edifice of the Anti-Counterfeiting Trade Agreement (ACTA) seems to have crumbled. This time, however, it happened in Europe.” (P.1) Legislation on a global scale is difficult in itself, but when the laws, themselves are faced with widespread protest, it becomes even more complicated.
Much of the world’s population has fought bills such as these, because they are considered to be intrusive and enable censorship. Many are concerned about the sheer reach of these new laws, “Some governments, such as those of Poland, Slovakia and Slovenia, see the agreement as a potential violation of privacy and an abdication of users' rights.”(P.12) This could cause major problems in international politics and I believe the most dramatic problems with global legislation is yet to come. “But ACTA could be just the beginning. In the coming years, the European political landscape will be a particularly fertile testing ground for the emergence of privacy, Internet-freedom and users' rights as a tenet of foreign policy and domestic politics.” (P.13)
Unfortunately, internet piracy has become such a common theme in media that it has reached the international arena. Legislation in many countries has been modified to include bills and amendments that discuss guidelines, definitions and consequences for internet piracy and copyright infringement. The Atlantic had this to say about it: “In the wake of the public outcry in the United States over proposed domestic antipiracy legislation, the Stop Online Piracy Act (SOPA) and the Protect IP Act (PIPA), international regulation is also taking a hit. The edifice of the Anti-Counterfeiting Trade Agreement (ACTA) seems to have crumbled. This time, however, it happened in Europe.” (P.1) Legislation on a global scale is difficult in itself, but when the laws, themselves are faced with widespread protest, it becomes even more complicated.
Much of the world’s population has fought bills such as these, because they are considered to be intrusive and enable censorship. Many are concerned about the sheer reach of these new laws, “Some governments, such as those of Poland, Slovakia and Slovenia, see the agreement as a potential violation of privacy and an abdication of users' rights.”(P.12) This could cause major problems in international politics and I believe the most dramatic problems with global legislation is yet to come. “But ACTA could be just the beginning. In the coming years, the European political landscape will be a particularly fertile testing ground for the emergence of privacy, Internet-freedom and users' rights as a tenet of foreign policy and domestic politics.” (P.13)
Global Conflict in The Age of Technology and Internet Piracy Part III
CBSnews.com Article on SOPA and PIPA
I, personally, find the consequences of internet piracy to be quite steep and unreasonable in many countries. The consequences change depending on how many times your file(s) have been downloaded and also how many file(s) were distributed. The United States, for example attempted to pass several bills giving the US government the power to censor sites that could potentially be a hub for copyright infringement. CBSnews.com included an article of the SOPA and PIPA protests and general information that is useful is deciding for yourself. In the article, SOPA, PIPA: What you need to know, “SOPA and PIPA...target the platform -- that is, the site hosting the unauthorized content...The bills would give the Justice Department the power to go after foreign websites willfully committing or facilitating intellectual property theft...The government would be able to force U.S.-based companies, like Internet service providers, credit card companies and online advertisers, to cut off ties with those sites.” (P.7-8) These legislations were met with a public outcry of censorship and certain websites (such as Reddit, Wikipedia, Mozilla, WordPress, and TwitPic), as a protest, participated in a 24-hour internet blackout. This social phenomenon put the bills “on-ice” so to speak.
I, personally, find the consequences of internet piracy to be quite steep and unreasonable in many countries. The consequences change depending on how many times your file(s) have been downloaded and also how many file(s) were distributed. The United States, for example attempted to pass several bills giving the US government the power to censor sites that could potentially be a hub for copyright infringement. CBSnews.com included an article of the SOPA and PIPA protests and general information that is useful is deciding for yourself. In the article, SOPA, PIPA: What you need to know, “SOPA and PIPA...target the platform -- that is, the site hosting the unauthorized content...The bills would give the Justice Department the power to go after foreign websites willfully committing or facilitating intellectual property theft...The government would be able to force U.S.-based companies, like Internet service providers, credit card companies and online advertisers, to cut off ties with those sites.” (P.7-8) These legislations were met with a public outcry of censorship and certain websites (such as Reddit, Wikipedia, Mozilla, WordPress, and TwitPic), as a protest, participated in a 24-hour internet blackout. This social phenomenon put the bills “on-ice” so to speak.
Global Conflict in The Age of Technology and Internet Piracy Part II
**Infographic of Internet Piracy Statistics**
Acquiring files is easy enough if you know where to look. According to a study researched by GO-GLOBE.com Web Technologies over 70% of online users believe that there is nothing wrong with internet piracy (Section I). Many interesting statistics show up in this well-designed infographic, such as 22% of all global internet bandwidth is used for internet piracy (Section I). Feel free to check out the interesting statistics for yourself.
The question I ask is why copyright infringement and internet piracy were at the forefront of international politics as of this time last year. The reason, in my opinion, is that many governments were afraid of the monetary consequences that piracy bestows on a country. It is estimated that a total of $12.5 billion is lost every year due to internet piracy. If the internet had been left to be completely fluid and organic without any repercussions, would we be seeing the same internet today? I don’t believe so.
Acquiring files is easy enough if you know where to look. According to a study researched by GO-GLOBE.com Web Technologies over 70% of online users believe that there is nothing wrong with internet piracy (Section I). Many interesting statistics show up in this well-designed infographic, such as 22% of all global internet bandwidth is used for internet piracy (Section I). Feel free to check out the interesting statistics for yourself.
The question I ask is why copyright infringement and internet piracy were at the forefront of international politics as of this time last year. The reason, in my opinion, is that many governments were afraid of the monetary consequences that piracy bestows on a country. It is estimated that a total of $12.5 billion is lost every year due to internet piracy. If the internet had been left to be completely fluid and organic without any repercussions, would we be seeing the same internet today? I don’t believe so.
Global Conflict in The Age of Technology and Internet Piracy Part I
**The Powerpoint Link**
With the creation of the internet, the ability to send and receive files has dramatically affected how the entertainment industry does business. The creation of Itunes and other programs like it with MP3-based media have become more popular than physical CDs and DVDs. Along with this boom in multimedia, the creation of websites that host files has also grown exceedingly thus, internet piracy was born. The first question many people ask is what exactly is internet piracy; in order to answer this question, I enlisted the aid of Armstrong Atlantic State University and a powerpoint published on their website (See Link Above). According to the powerpoint, internet piracy is the unauthorized obtainment of digital materials by hosting or transferring files. (Slide 2). The most common files transferred are video and audio files (MP3s, MP4s, AVIs, etc.) pictures (JPEGs, PDFs, PNGs) and software (Slide 3-4). There are many consequences to these acts, however it varies depending on the country. This lack of uniformity tends to cause friction.
With the creation of the internet, the ability to send and receive files has dramatically affected how the entertainment industry does business. The creation of Itunes and other programs like it with MP3-based media have become more popular than physical CDs and DVDs. Along with this boom in multimedia, the creation of websites that host files has also grown exceedingly thus, internet piracy was born. The first question many people ask is what exactly is internet piracy; in order to answer this question, I enlisted the aid of Armstrong Atlantic State University and a powerpoint published on their website (See Link Above). According to the powerpoint, internet piracy is the unauthorized obtainment of digital materials by hosting or transferring files. (Slide 2). The most common files transferred are video and audio files (MP3s, MP4s, AVIs, etc.) pictures (JPEGs, PDFs, PNGs) and software (Slide 3-4). There are many consequences to these acts, however it varies depending on the country. This lack of uniformity tends to cause friction.
Cuban Missile Crisis- Global Conflict.
 |
| http://www.csmonitor.com/Commentary/Opinion/2012/1015/50-years-after-Cuban-missile-crisis-closer-than-you-thought-to-World-War-III |
Why was the Cuban Missile Crisis a global conflict?
The U.S never knew what a problem nuclear weapons were. They were being developed all over the world but no one had been threatened with them. The President and his advisors realized that something had to be done in order to protect themselves and the U.S citizens.
I can't imagine how scary it must have been to fear something that you don't quite understand yet.
Biofuel from Algae grown in wastewater
Look at the picture on the link above; can you see
yourself filing up your car tank with biofuel from Algae grown on wastewater?
Algae may hold the greatest potential
for simultaneously tackling the problems of our worldwide dependence on fossil
fuels and limiting CO2 emissions linked to global climate change.
Algae can produce substantially greater oil per acre than traditional oil seeds
and also cut the level of CO2 as algae consume it while emitting
clean oxygen. Algae can grow in places other than on farmlands or other
arable land. Many strains of algae can grow optimally using brackish water, seawater,
or wastewater. For these reasons and others, Algae have many advantages
over other types of plants in addressing some of the world’s major challenges
for energy security, reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and need for
sustainability.
Results of the Cuban Missile Crisis
1963- A telephone hotline was set up between the U.S and the Soviet Union.
Provided instant contact between the two presidents.
1963- The Nuclear test ban treaty was signed
- Ban on testing in the atmosphere, space, or underwater
- Did allow testing underground
- ALL TO WORK ENDING THE ARMAMENTS RACE
1968- The Nuclear non- proliferation treaty was signed
Link to text of the Treaty : http://www.un.org/disarmament/WMD/Nuclear/NPTtext.shtml
- The superpowers agreed to not supply nuclear technologies to other countries
- On 11 May 1995, the Treaty was extended indefinitely.
- A total of 190 parties have joined the Treaty, including the five nuclear-weapon States including the U.S, Russia, U.K, France, and China.
The Soviet Union:
Khrushchev claimed that he had won and both of his goals had been accomplished.
- U.S never bothered Cuba
- Missile sites in Turkey were dismantled * Kept a secret*
Biomass – A Sustainable Renewable Energy Source
The term "biomass" refers to organic matter
that has stored energy through the process of photosynthesis. The Link below
briefly explains the benefits of using Biomass; also the pictures on the slide
show are very descriptive. http://www.energy.siemens.com/us/en/powergeneration/renewables/biomass-power/
Many of the biomass fuels used today come in the form
of wood products, dried vegetation, crop residues, and aquatic plants. Biomass
is one of the most plentiful and well-utilized sources of renewable energy in
the world.
If the contribution of biomass to the world energy
economy is to grow, technological innovations will be needed, so that biomass
can be converted to usable energy in ways that are more efficient, less
polluting, and at least as economical as today's practices.
When we have enough government support and have and enough
land for the continuous growth of energy crops
for biomass-based energy, we may have a successful form of
alternative energy. But as long as worldwide prices of coal, oil and gas are
relatively low, the establishment of plantations dedicated to supplying
electric power or other higher forms of energy will occur only where financial
subsidies or incentives exist or where other sources of energy are not
available. Although it is currently utilized across the globe, biomass energy
is clearly not capable of sustaining the world's energy needs on its own.
Action Taken - Cuban Missile Crisis
 |
| http://ivarfjeld.wordpress.com/2011/07/01/israel-can-sink-hostile-ships-at-ports-of-origin/ |
Kennedy had explained that the nuclear missile bases were in Cuba to provide a nuclear-strike capability against the western hemisphere. He essentially had five options
| 1 | He could do nothing and ignore the missiles. This would have been political suicide and if the Russians had seen this as weakness on his part, they could have taken advantage of it. |
| 2 | He could order a full scale military invasion of Cuba. This could lead to heavy US casualties and that would be politically damaging. It would almost certainly involve Russian casualties which could escalate the problem. The American chiefs-of-staff were not convinced that it would be successful either especially as the offending missile bases were in remote areas and most were well inland. |
| 3 | He could order an air strike against the missile bases only. The problem again would be Russian casualties and the Air Force was not sure it could deliver pin-point bombing raids on what were relatively small targets. |
| 4 | He could call on the Russians to remove the missiles explaining the damage their presence was doing to Russian/American relations. However, the Russians were highly unlikely to listen to a ‘polite’ request especially as they even refused to recognise the existence of the missiles at the United Nations emergency meeting on the matter. |
| 5 | He could put a naval blockade around the island - quarantine it - and not allow any more Russian ships to enter Cuba. This would still leave missiles on Cuba but the negotiations would continue in the background while publically Kennedy would be seen to be doing something specific. |
http://www.historylearningsite.co.uk/cuban_missile_crisis.html
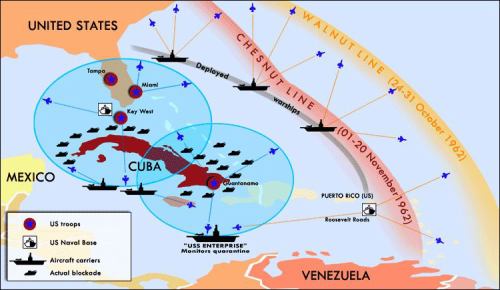
The president ordered a naval quarantine of Cuba, the initial line was set up on October 24th 1962 ( Shown above). A quarantine would allow for the inspection of incoming Soviet ships to ensure that there were no missile parts being transported. The benefit of the quarantine was that if something were to occur, the responsibility would be placed on the Soviet Union. By the time the quarantine was lifted in November there was an aircraft carrier, two cruisers, 22 destroyers, and two missile frigates.
The President was advised against using a naval quarantine/blockade, and was in fact urged to launch and air attack. Kennedy's decision was not what was expected, in the long run it was the smartest choice! If an air attack was ordered the Soviet Union would have seen this as an act of war, no one wants to go through another war! Especially if nuclear bombs would have been involved on both sides.
Who, What, When, Where and
Why?
The
country of Kosovo was once part of the southern part of Serbia. The majority of the population is of Albanian
descent and is of Muslim heritage. The
area was largely autonomous until 1989 when the results of the dictatorship of
Slobodan Milosevic would forever alter the region by bringing under control of
the Serbian capital of Belgrade. I read
the historical overview done by NATO which said this of the conflict, “During
1998, open conflict between Serbian military and police forces and Kosovar
Albanian forces resulted in the death of over 1500 Kosovar Albanians and forced
400,000 people from their homes.” These
numbers seem relatively small when compared to other wars, but what has to be
considered is lingering stigma of having to recreate themselves when they truly
were not an independent country in the first place. The war destroyed so much of the
infrastructure and the physical damage was severe. What we consider to be primitive by today’s
standards is considered luxury by the people of Kosovo. Can you imagine the issues of a population
struggling to emerge from the atrocities of the war in order to regain a sense
of normalcy?
Here are some startling
figures from NATO:
·
Between
March 1998 and March 1999, before NATO governments decided upon military
action, over 2000 people were killed as a result of the Serb government's
policies in Kosovo.
·
During
the summer of 1998, a quarter of a million Kosovar Albanians were forced from
their homes as their houses, villages and crops were destroyed.
·
In
January 1999, evidence was discovered, by a United Nations humanitarian team,
of the massacre of over 40 people in the village of Racak.
·
By
the beginning of April 1999, the United Nations High Commission for Refugees
estimated that the campaign of ethnic cleansing had resulted in 226,000
refugees in Albania, 125,000 in the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia and
33,000 in Montenegro.
·
Assistance
given by NATO forces to alleviate the refugee situation included providing
equipment and building camps to house 50,000 refugees in Albania; assistance in
expanding camps in the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia; providing medical
support and undertaking emergency surgery on the victims of shootings by Serb
forces; transporting refugees to safety; and providing transport for
humanitarian aid and supplies.
·
By
the end of May 1999, over 230,000 refugees had arrived in the former Yugoslav Republic
of Macedonia, over 430,000 in Albania and some 64,000 in Montenegro.
Approximately 21,500 had reached Bosnia and over 61,000 had been evacuated to
other countries. Within Kosovo itself, an estimated 580,000 people had been
rendered homeless.
·
It
is estimated that by the end of May, 1.5 million people, i.e. 90% of the
population of Kosovo, had been expelled from their homes. Some 225,000 Kosovar
men were believed to be missing. At least 5000 Kosvars had been executed.
·
NATO
forces have flown in many thousands of tons of food and equipment into the
area. By the end of May 1999, over 4666 tons of food and water, 4325 tons of
other goods, 2624 tons of tents and nearly 1600 tons of medical supplies had
been transported to the area.
Before & During The Conflct 1998-1999
1998-1999
Life in Kosovo
 |
The
genocide of this period was strikingly similar to previous Serbian campaigns in
Bosnia. This must have been horrible to
live through. The male population was
targeted for mass execution, detention and torture. Young women were easy targets for sex crimes
and the remainder of the population was affected by what was going on. My nephew Skender was a teenager during this
time and I have only heard tidbits of his story and what life was like for his
family. One can only imagine what life
was like. When I really considered the
horrors experienced during this time and the need to fight for sustenance and
survival made me grateful for what we have here in the United States. We really don’t have a clue. We may feel needy, but we really don’t know
what it is to need in the face of conflict and war on an everyday basis.
 |
|
Albanian war crimes in the Serbian Province of Kosovo 1998-1999
480 x 360 | 16 KB
|
 |
|
The Kosovo War (1998–1999)
700 x 447 | 171.7 KB
|
 |
|
The defining images of our turbulent times | Photography |
Agenda ...
787 x 550 | 266.8 KB
|
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)